딸기 혈관종(모세 혈관종/딸기양 혈관종), Strawberry hemangioma(Capillary hemangioma/Strawberry nevus)
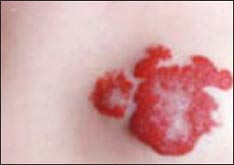
사진485. 딸기 혈관종.
Copyrightⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee,MD.. FAAP
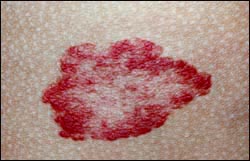
사진 486. 딸기 혈관종이 자연히 더 나아가는 과정.
Copyrightⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
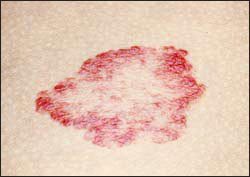
사진 487. 딸기 혈관종이 자연히 나아가는 과정.
Copyrightⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee,MD, .FAAP
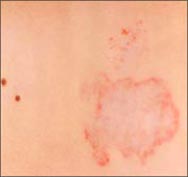
사진 488. 딸기 혈관종이 자연히 거의 다 나아가는 과정.
Copyrightⓒ 2001 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
- 딸기 혈관종은 빨간 딸기색과 같이 혈관종이 빨갛고, 피부의 표면 위로 현저히 솟아 나 있고, 혈관종의 경계가 뚜렷한 혈관성 모반의 일종이다.
- 혈관성 모반 중 가장 흔한 종류이다.
- 딸기 혈관종을 딸기양 모반, 딸기 혈관종, 또는 모세 혈관종이라고도 한다(사진 485~488 참조)
- 딸기 혈관종은 출생 후 바로 육안으로 볼 수 있을 정도로 확연히 나타나기도 한다.
- 그렇지만 대부분의 경우 생후 1~2개월 경 더 현저히 나타나기 시작한다.
- 그 후부터는 점점 더 현저히 나타나고, 또 점점 더 커지다가 생후 1~2세경부터 점점 작아지기 시작한다.
- 그 후 계속 점점 더 작아지다가 7~8세경에는 자연히 완전히 없어지는 것이 자연 진행 과정이다.
- 딸기 혈관종에서 이런 자연 진행 과정을 따르는 빈도는 70~80% 정도이다.
- 전 딸기 혈관종의 70~80%는 7~8세경에 자연히 없어진다.
- 신체의 어느 부위의 피부에도 생길 수 있지만 얼굴, 머리, 가슴, 사지 등의 피부에 더 잘 난다.
딸기 혈관종(모세 혈관종/딸기양 혈관종) 증상 증후
- 대부분의 딸기 혈관종은 아무 증상이 없고 보기에 이상할 뿐이다.
- 그렇지만 눈꺼풀이나 콧구멍 근처, 또는 귓구멍 근처에 크게 나서 그 부위에 있는 귓구멍, 콧구멍을 막아 그로 인해 그 기관의 기능에 장애가 생길 수 있다.
- 안구 주위에 난 딸기 혈관종으로 안구가 가려지면 그 가려진 정도에 따라 약시 등 시야장애가 생길 수 있다.
- 기저귀를 채우는 부위에 난 딸기 혈관종에 궤양이 생기기 쉽다.
- 궤양이 생긴 혈관종에 세균 감염이 생길 수 있고 또 혈관종 궤양에서 출혈할 수 있다.
- 턱수염이 나는 부위에 딸기 혈관종이 나 있으면 기도 속에도 혈관종이 나 있을 확률이 63% 정도나 된다.
- 코 끝 부분에 난 딸기 혈관종이나 입술에 난 딸기 혈관종은 미관상 문제가 될 수 있다.
- 손에 난 딸기 혈관종을은 손 기능 장애가 생길 수 있다.
- 딸기 혈관종이 신생아에게 많이 나 있을 때는 그들의 간, 폐, 뇌, 소화기 등, 내부 장기에도 혈관종이 나 있을 가능성이 있다
- 일반적으로 딸기양 모반은 신생아기 동안에는 아주 작지만 생후 1~2년 간 점점 더 커지고 색깔도 점점 더 빨갛게 변하는 것이 보통이다.
- 그렇지만 생후 1~2년 이후부터 딸기 혈관종이 점점 더 작아지기 시작해서 3세에 30%, 5세에 50%, 9세에 90% 이상이 자연히 사라지는 것이 보통이다.
딸기 혈관종(모세 혈관종/딸기양 혈관종) 치료
- 대부분의 딸기 혈관종은 생후 1~2년이 지난 후부터 생후 7세 까지 몇 년간을 거쳐 점점 작아지면서 자연히 사라진다.
- 따라서 대개의 경우 두고 관찰적 치료를 하는 것이 보통이다.
- 귓구멍이나 콧구멍의 주위에 나서 귓구멍이나 콧구멍을 막아 그 기관의 기능 장애를 일으키는 딸기 혈관종이나, 눈꺼풀이나 눈 주위에 나서 안구를 가리는 딸기 혈관종, 호흡기에 난 딸기 혈관종, 궤양성 혈관종 등 기능장애를 일으키는 딸기 혈관종은 의사의 처방에 따라 전신 경구용 코르티코스테로이드제로 몇 개월 동안 치료하기도 하고 전신 펄스드 혈관 코르티코스테로이드제 치료를 할 수 있다.
- 전신 경구용 코르티코스테로이드제로 치료한 결과가 전신 혈관 코르티코스테로이드제로 치료한 결과 보다 더 낫지만 부작용이 더 많다고 한다.
- 전신 경구용 코르티코스테로이드제 치료의 효과는 8% 정도 된다고 한다.
- 그 외 레이저 치료, 또는 Interferon-알파 치료도 한다.
- 딸기 혈관종의 5~15%에서 혈관종에 궤양이 생길 수 있다.
- 궤양의 정도에 따라 항생제 연고나 크림으로 치료하거나, 외과적 수술치료, 펄스드 다이 레이저 치료, 국소 코르티 코르티코스테로이드제 주사와 전신 코르티코스테로이드제로 치료하기도 한다.
- 그 밖의 신체 다른 피부에 생긴 것은 나이에 따라 점점 더 커지다가 자연히 없어지므로 그대로 놓고 관찰한다.
- Hemangioma(propranolol hydrochloride으로 치료할 수도 있다. 참조 문헌 Hemangioma, AAP News 11/2014.
- 혈관종을 propranolol로 치료 하면 치료가 잘 도기도 하지만 치료를 중지 하면 재발 되기도 한다. Pediatrics. 4/2016
혈관종의 합병증 Complications of Hemangioma
- 대부분의 혈관종은 합병이 생기지 않으나 때로는 다음과 같은 합병증이 생길 수 있다.
- 혈관종에 궤양이 생길 수 있다.
- 가장 흔히 볼 수 있는 합병증이다.
- 궤양이 생기면 아플 수 있고 거기에 박테리아 감염이 생길 수 있고 출혈도 생길 수 있다. 궤양이 나은 후 상흔이 생길 수 있다.
- 봉소염, 골수염, 또는 패혈증도 생길 수 있다.
- 혈관종이 외이도 입구에 생기면 중이염도 생길 수 있고 소리 전도 장애 난청이 생길 수 있다.
- 안구 주위에 혈관종이 생겨 안구와 시야가 막히면 약시 또는 난시가 생길 수 있다.
- 혈관종이 안면에 여러 개 나 있을 때나 상당히 큰 혈관종이 안면에 나 있으면 혈관종이 간이나 호흡기계, 또는 비뇨생식기계에도 혈관종이 나 있을 수 있다.
- 큰 혈관종이 안면에 나 있을 때 두개 강내 혈관종이 나 있을 수 있다.
- 턱, 입술, 하악, 목 등에 혈관종이 나 있으면 성문에도 혈관종이 나 있을 수 있다.
- 요천추 부위의 피부에 혈관종이 나 있으면 척수, 항문직장, 비뇨생식기계에도 혈관종이 나 있을 수 있다.
- 카사바하-메리트 증후군도 생길 수 있다.
- 그 외
혈관종의 진단 치료
- 병력, 증상 징후, 검진, 피검사, 울트라사운드 검사로 진단한다.
Strawberry hemangioma (Capillary hemangioma/Strawberry nevus)

Picture 485. Strawberry hemangioma. Copyrightⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD.. FAAP

Photo 486. Natural progression of strawberry hemangioma. Copyrightⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 487. Natural progression of strawberry hemangioma. Copyright© 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, .FAAP

Picture 488. Strawberry hemangioma is the natural progression of almost all. Copyrightⓒ 2001 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Strawberry hemangioma is a type of vascular nevus with a red hemangioma like a red strawberry, prominently protruding above the surface of the skin, and clearly demarcated by the hemangioma.
• The most common type of vascular nevus.
• Strawberry hemangioma is also called a strawberry nevus, strawberry hemangioma, or capillary hemangioma (see photos 485-488).
• Strawberry hemangiomas are often visible to the naked eye right after birth. • However, in most cases, it begins to appear more prominently around 1 to 2 months of age.
• After that, it appears more and more conspicuously, and it gets bigger and starts to get smaller around 1~2 years old
. • After that, it continues to get smaller and disappears completely around the age of 7 or 8, which is a natural process.
• Strawberry hemangiomas follow this spontaneous process in 70-80% of cases.
• 70-80% of all strawberry hemangiomas disappear spontaneously around the age of 7-8.
• It can appear on the skin anywhere on the body, but is more common on the skin on the face, head, chest, and extremities.
Strawberry Hemangioma (Capillary Hemangioma/Strawberry Hemangioma) Symptoms, signs
• Most strawberry hemangiomas are asymptomatic and look strange.
• However, large eyelids, near the nostrils, or near the ear canal can block the ear canal or nostril in that area, which may cause dysfunction of the organ.
• If the eyeball is obscured by a strawberry hemangioma that grows around the eyeball, vision problems such as amblyopia may occur depending on the degree of occlusion.
• Strawberry hemangiomas in the diaper area are prone to ulceration.
• Bacterial infection can develop in the ulcerated hemangioma, and bleeding can occur in the hemangioma ulcer.
• If there is a strawberry hemangioma in the area of the beard, there is a 63% chance that the hemangioma also exists in the airway.
• Strawberry hemangioma on the tip of the nose or strawberry hemangioma on the lips can be a cosmetic problem. • Strawberry hemangioma on the hand can cause hand dysfunction.
• When strawberry hemangiomas are prevalent in newborns, it is possible that their liver, lungs, brain, and digestive organs may also have hemangioma. • Strawberry-like nevus is usually very small during newborns, but usually gets bigger and more reddish during the first year or two of life.
• However, from 1 to 2 years of age, strawberry hemangiomas start to get smaller and usually disappear spontaneously by 30% at 3 years old, 50% at 5 years old, and over 90% at 9 years old.
Treatment of Strawberry Hemangioma (Capillary Hemangioma/Strawberry Hemangioma)
• Most strawberry hemangiomas disappear spontaneously from 1 to 2 years of age to 7 years of age as they become smaller and smaller.
• Therefore, in most cases, it is normal to leave it and perform the observational treatment.
• Strawberry hemangioma that occurs around the ear canal or nostril and blocks the ear or nostril and causes dysfunction of the organ; Strawberry hemangioma that causes corticosteroids can be treated with systemic oral corticosteroids for several months or systemic pulsed vascular corticosteroids according to the doctor’s prescription.
• The results of treatment with systemic oral corticosteroids are better than those of systemic vascular corticosteroids, but they have more side effects.
• The effectiveness of systemic oral corticosteroid treatment is said to be about 8%.
• Other laser treatments, or Interferon-alpha treatments.
• In 5 to 15% of strawberry hemangiomas, the hemangioma can be ulcerated.
• Depending on the severity of the ulcer, it may be treated with antibiotic ointment or cream, surgical treatment, pulsed die laser treatment, topical corticosteroid injection, and systemic corticosteroid treatment.
• Other skin formations on the body grow larger with age and disappear naturally, so leave it as it is and observe it.
• Hemangioma (can also be treated with propranolol hydrochloride. References Hemangioma, AAP News 11/2014.
Complications of Hemangioma
• Most hemangiomas do not cause complications, but sometimes the following complications may occur.
• Hemangiomas may become ulcerated.
• This is the most common complication.
• Ulcers can be painful, bacterial infections, and bleeding. After the ulcer heals, scarring may form.
• Cellulitis, osteomyelitis, or sepsis may also develop.
• If the hemangioma occurs at the entrance to the external auditory meatus, otitis media may also occur, and sound conduction disturbance may cause hearing loss.
• Amblyopia or astigmatism can occur when a hemangioma around the eye blocks the eye and vision.
• If there are multiple hemangiomas on the face, or if there are very large hemangiomas on the face, the hemangioma may also be present in the liver, respiratory system, or genitourinary system.
• An intracranial hemangioma may be present when a large hemangioma is present on the face.
• If there are hemangiomas on the jaw, lips, mandible, or neck, the glottis may also have hemangiomas.
• If the skin of the lumbar sacrum has hemangioma, the spinal cord, anorectum, and genitourinary system may also have hemangioma.
• Cassavaja-Merritt syndrome may also develop.
• etc
Diagnosis, treatment of hemangioma
• Diagnosis is made by medical history, symptom signs, examination, blood test, and ultrasound test.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy of Pediatrics
- Rebound Growth of Infantile Hemangioma After Propranolol Therapy. Pediatrics. 4/2016
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.